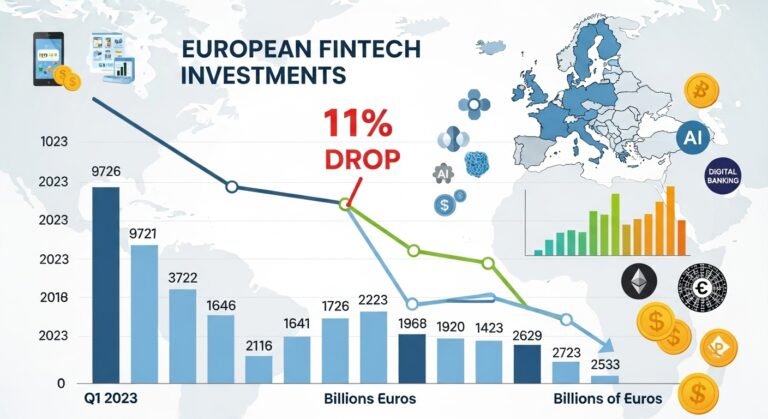
European FinTech Investments Drop 11% YoY in 2025, marking a notable shift in the continent’s once high-flying financial technology landscape. After years of record-breaking venture capital inflows and aggressive expansion across digital banking, payments, and blockchain services, the sector entered a more cautious phase. Investors, founders, and regulators alike began to recalibrate expectations as economic volatility, geopolitical tensions, and tightening capital conditions reshaped the investment environment.
Throughout the early 2020s, Europe positioned itself as a global powerhouse for financial innovation. Cities such as London, Berlin, Paris, and Amsterdam became hubs for digital banking, payment innovation, open banking platforms, and blockchain finance startups. However, the 11% year-over-year drop in funding in 2025 highlights a broader transformation within the market, one driven by rising interest rates, investor risk aversion, and the shift from growth-at-all-costs to profitability-focused strategies.
Despite the slowdown, the European FinTech ecosystem remains one of the most dynamic globally. The decline in funding does not necessarily signal weakness; instead, it reflects a transition toward sustainable growth, stricter valuation discipline, and a maturing market. Understanding why European FinTech investments dropped by 11% YoY amid market uncertainties in 2025 requires a closer look at the macroeconomic environment, investor sentiment, sector-specific challenges, and emerging opportunities shaping the industry’s future.
European FinTech Investments Drop 11%
Before the downturn, Europe experienced an unprecedented surge in venture capital funding, digital financial services, and FinTech innovation. Between 2018 and 2023, the region saw record levels of investment, fueled by low interest rates, abundant liquidity, and strong consumer adoption of digital financial solutions.
European FinTech startups thrived in areas such as neobanking, cross-border payments, buy now pay later (BNPL) services, and cryptocurrency platforms. These sectors attracted significant investor interest as they promised to disrupt traditional banking models and generate rapid user growth.
The Role of Pandemic-Era Acceleration
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of contactless payments, mobile banking, and remote financial services. Consumers and businesses alike turned to digital solutions, creating a surge in demand for FinTech products.
This demand translated into strong investment activity. Many startups raised large funding rounds at high valuations, often based on aggressive growth projections rather than proven profitability. While this approach fueled innovation, it also created valuation bubbles that would later be corrected.
Why European FinTech Investments Dropped by 11% YoY in 2025
Macroeconomic Pressures and Interest Rate Hikes
One of the primary reasons European FinTech investments dropped by 11% YoY amid market uncertainties in 2025 was the global macroeconomic environment. Central banks across Europe raised interest rates to combat inflation, increasing the cost of capital and reducing investor appetite for high-risk assets.
Higher interest rates made traditional investments such as bonds more attractive, pulling capital away from venture-backed startups and speculative growth sectors. As a result, funding rounds became smaller, valuations dropped, and many startups struggled to secure new investment.
Shift from Growth to Profitability
Another key factor behind the funding decline was the shift in investor priorities. During the boom years, investors focused heavily on user acquisition, market share, and rapid scaling. By 2025, the narrative changed.
Investors began demanding clear paths to profitability, sustainable revenue models, and strong unit economics. Startups that previously relied on heavy spending to acquire customers found it harder to justify their valuations. This shift significantly reduced funding for early-stage companies with unproven business models.
Geopolitical Tensions and Market Volatility
Geopolitical uncertainties also contributed to the investment slowdown. Ongoing global conflicts, trade disruptions, and political instability created an unpredictable economic environment. Investors became more cautious, prioritizing stability over aggressive expansion.
Currency fluctuations and regional economic disparities across Europe added another layer of complexity. Some markets performed better than others, leading investors to concentrate funding in a smaller number of high-quality startups rather than spreading capital across the ecosystem.
Sector-by-Sector Impact of the Funding Decline
Digital Banking and Neobanks
The neobank sector was among the most affected by the funding slowdown. Many digital banks had expanded rapidly in previous years, offering low-cost or free services to attract customers. However, rising interest rates and increased competition made profitability more challenging.
As European FinTech investments dropped by 11% YoY amid market uncertainties in 2025, several neobanks faced down rounds, restructuring efforts, or delayed expansion plans. Investors became more selective, favoring institutions with diversified revenue streams and strong balance sheets.
Payments and Cross-Border Solutions
The payments sector proved more resilient than others. Demand for real-time payments, cross-border transactions, and merchant solutions remained strong, driven by the continued growth of e-commerce and digital trade.
However, even in this segment, funding rounds became more conservative. Investors prioritized companies with established customer bases and predictable revenue streams rather than speculative payment innovations.
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Startups
The crypto market volatility of previous years had a lasting impact on investor sentiment. While blockchain infrastructure and tokenization platforms continued to attract interest, speculative crypto projects struggled to raise funds. Regulatory scrutiny across Europe also affected the sector. New compliance requirements increased operational costs, making it harder for early-stage crypto startups to secure investment.
Regional Differences Across Europe
Western Europe’s Mature Markets
Countries such as the United Kingdom, Germany, and France remained the primary destinations for FinTech funding. These markets benefit from established financial ecosystems, strong regulatory frameworks, and large consumer bases. However, even these mature markets felt the effects of the 11% decline. Late-stage funding rounds were particularly impacted, as investors grew cautious about high valuations.
Emerging FinTech Hubs in Eastern and Southern Europe
Despite the overall downturn, some emerging markets continued to attract attention. Countries in Eastern and Southern Europe offered lower operational costs, strong technical talent, and growing digital adoption. These regions became attractive for early-stage investors seeking undervalued opportunities. As a result, while total investment volumes dropped, the geographic distribution of capital became more diverse.
The Role of Regulation in the 2025 Investment Climate
Stronger Compliance Requirements
European regulators continued to push for stricter compliance standards, particularly in areas such as anti-money laundering (AML), data protection, and consumer protection. While these regulations improved market stability, they also increased operational costs for startups.
For many early-stage companies, meeting regulatory requirements required significant resources. This reduced their attractiveness to investors seeking quick returns.
The Impact of Open Banking and PSD2
On the positive side, Europe’s commitment to open banking and regulatory frameworks such as PSD2 continued to foster innovation. These policies encouraged competition, enabled new business models, and supported the growth of API-driven financial services.
Even as European FinTech investments dropped by 11% YoY amid market uncertainties in 2025, regulatory support for innovation ensured that the sector retained strong long-term potential.
Investor Behavior and Funding Trends
Fewer Mega Rounds
One of the most visible changes in 2025 was the decline in mega funding rounds. Deals exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars became less common, reflecting investor caution. Instead, funding was distributed across smaller, more strategic investments. Investors focused on startups with proven traction, strong leadership, and clear profitability timelines.
Rise of Strategic and Corporate Investors
As traditional venture capital slowed, corporate venture arms, banks, and payment companies played a larger role in FinTech funding. These investors often pursued strategic partnerships rather than purely financial returns. This shift helped stabilize the market, as strategic investors brought industry expertise and long-term commitment.
Startup Strategies in a Tougher Funding Environment
Cost Optimization and Efficiency
With funding harder to secure, many startups focused on cost optimization, operational efficiency, and sustainable growth. Layoffs, budget cuts, and restructuring became more common across the sector.
While these measures were challenging, they helped many companies extend their runway and move closer to profitability.
Focus on Core Products
Startups also began narrowing their focus, prioritizing core products over rapid expansion into new markets or services. This approach allowed companies to strengthen their value propositions and improve financial performance.
Opportunities Emerging from the Downturn
Valuation Corrections Create Entry Points
The 11% decline in European FinTech investments created opportunities for investors willing to take a long-term view. Lower valuations allowed new entrants to acquire stakes in promising startups at more reasonable prices. This correction also reduced speculative investments, leading to a healthier and more sustainable ecosystem.
Growth in B2B FinTech Solutions
Business-focused FinTech solutions gained traction during the downturn. Areas such as embedded finance, SME lending, and financial infrastructure attracted growing investor interest. These sectors offered more predictable revenue streams compared to consumer-focused apps, making them attractive during uncertain times.
Long-Term Outlook for European FinTech
A Shift Toward Sustainable Growth
While European FinTech investments dropped by 11% YoY amid market uncertainties in 2025, the long-term outlook remains positive. The industry is transitioning from a phase of rapid expansion to one focused on sustainable growth and profitability. This shift is expected to produce stronger, more resilient companies capable of weathering economic cycles.
Continued Innovation and Adoption
Digital financial services continue to gain popularity across Europe. From AI-driven financial tools to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, innovation remains a defining feature of the sector. As economic conditions stabilize, investment activity is likely to rebound, particularly in areas with strong regulatory support and clear business models.
Conclusion
European FinTech investments dropped by 11% YoY amid market uncertainties in 2025, reflecting a broader shift in the global investment landscape. Rising interest rates, geopolitical tensions, and changing investor priorities led to more cautious funding strategies and a focus on profitability.
However, the decline does not signal the end of European FinTech growth. Instead, it marks a transition toward a more mature, disciplined, and sustainable ecosystem. With strong regulatory support, continued digital adoption, and emerging opportunities in B2B solutions and infrastructure, the sector remains well-positioned for long-term success. As the market evolves, both investors and startups are adapting to new realities. The companies that survive this period of adjustment are likely to emerge stronger, more efficient, and better prepared for the next wave of financial innovation.
FAQs
Q: Why did European FinTech investments drop by 11% in 2025?
European FinTech investments dropped by 11% YoY amid market uncertainties in 2025 primarily due to rising interest rates, global economic volatility, and a shift in investor priorities. Investors became more cautious and focused on profitability rather than rapid growth, leading to smaller funding rounds and fewer mega deals.
Q: Which FinTech sectors were most affected by the funding decline?
Digital banking and neobanks were among the most affected sectors because many relied on aggressive expansion strategies without strong profitability. Cryptocurrency startups also faced challenges due to market volatility and increased regulatory scrutiny, while payments and infrastructure-focused companies proved more resilient.
Q: Is the drop in FinTech investment a sign of long-term decline?
The 11% drop does not necessarily indicate a long-term decline. Instead, it reflects a market correction and a shift toward more sustainable growth models. Many analysts believe the European FinTech ecosystem will continue to grow as economic conditions improve.
Q: How are FinTech startups adapting to the tougher funding environment?
Startups are focusing on cost efficiency, profitability, and core product development. Many companies have reduced spending, streamlined operations, and prioritized revenue-generating services to attract investors.
Q: What opportunities exist despite the investment slowdown?
The downturn has created opportunities in areas such as embedded finance, SME lending, and financial infrastructure. Lower valuations also provide attractive entry points for long-term investors seeking high-quality startups.